Physiological Aspects on Liver Fibrosis
Keywords:
Liver Fibrosis, liver damage, autoimmune liver diseasesAbstract
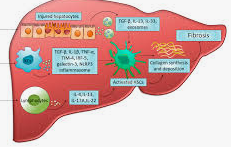
Liver fibrosis resulting from long-standing liver damage represents a major health care burden worldwide. To date, there is no anti-fibrogenic agent available, making liver transplantation the only curative treatment for decompensated cirrhotic liver disease. Liver fibrosis can result from different underlying chronic liver disease, such as chronic viral infection, excessive alcohol consumption, fatty liver disease or autoimmune liver diseases. It is becoming increasingly recognised that as a result from different pathogenic mechanisms liver fibrosis must be considered as many different diseases for which individual treatment strategies need to be developed. Moreover, the pathogenic changes of both liver architecture and vascularisation in cirrhotic livers, as well as the lack of "true-to-life" in vitro models have impeded the development of an effective anti-fibrogenic drug. Thus, in order to identify an efficient anti-fibrogenic compound, novel in-vitro models mimicking the interplay between pro-fibrogenic cell populations, immune cells and, importantly, the extracellular matrix need to be developed.
Downloads
References
Yu H, Shimakawa A, McKenzie CA, Brodsky E, Brittain JH, Reeder SB. Multiecho water-fat separation andsimultaneous R2* estimation with multifrequency fat spectrum modeling. Magn Reson Med. 2008
Tsuda E, Brännmark C, Palmér R, et al. A hierarchical whole-body modeling approach elucidates the linkbetween In Vitro insulin signaling and In Vivo glucose homeostasis. J Biol Chem. 2010:286(29):26028-41.
Yamda JM, Tymoczko JL, Stryer L. Biochemistry. 6th ed. New York, US: W. H. Freeman and Company,2011.
Lee A, Kreutz C, Maiwald T, et al. Structural and practical identifiability analysis of partially observeddynamical models by exploiting the profile likelihood. Bioinformatics. 2011;25(15):1923-9.
Watanabe L, Peeters F, Sinkus R, et al. Liver fibrosis: non-invasive assessment with MR elastography. NMRBiomed. 2011;19(2):173-9.
Ashyraliyev M, Xydeas T, Catheline S, Bercoff J, Fink M. Viscoelastic shear properties of in vivo breastlesions measured by MR elastography. Magn Reson Imaging. 2009;23(2):159-65.
Trauner M, Boyer JL. Bile salt transporters: molecular characterization, function, and regulation. Physiol Rev.2003;83(2):633-71.
Dawson PA, Lan T, Rao A. Bile acid transporters. J Lipid Res. 2009;50(12):2340-57.
Mahagita C, Grassl SM, Piyachaturawat P, Ballatori N. Human organic anion transporter 1B1 and 1B3function as bidirectional carriers and do not mediate GSH-bile acid cotransport. Am J Physiol GastrointestLiver Physiol. 2007;293(1):G271-8.
Gu X, Manautou JE. Regulation of hepatic ABCC transporters by xenobiotics and in disease states. DrugMetab Rev. 2010;42(3):482-538.
Gerk PM, Vore M. Regulation of expression of the multidrug resistance- associated protein 2 (MRP2) and itsrole In drug disposition. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002;302(2):407-15.
Meier Y, Pauli-Magnus C, Zanger UM, et al. Interindividual variability of canalicular ATP-binding-cassette(ABC)-transporter expression in human liver. Hepatology. 2006;44(1):62-74
Kullak-Ublick GA, Baretton GB, Oswald M, Renner EL, Paumgartner G, Beuers U. Expression of thehepatocyte canalicular multidrug resistance protein (MRP2) In primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatol Res.2002;23(1):78- 82.
Cheng Q, Aleksunes LM, Manautou JE, et al. Drug-metabolizing enzyme and transporter expression in amouse model of diabetes and obesity. Mol Pharm. 2008;5(1):77-91.
Rockey DC, Friedman SL. Hepatic Fibrosis and Cirrhosis. In: Boyer TD, Manns MP, Sanyal AJ, eds. Zakimand Boyer's Hepatology. Philadelphia, PA, USA: Elsevier Saunders, 2012; p. 64.
Batts KP, Ludwig J. Chronic hepatitis. An update on terminology and reporting. Am J Surg Pathol.1995;19(12):1409-17
Reddy JK, Rao MS. Lipid metabolism and liver inflammation. II. Fatty liver disease and fatty acid oxidation.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006;290(5):G852-8.
Baranova A, Lal P, Birerdinc A, Younossi ZM. Non-invasive markers for hepatic fibrosis. BMCGastroenterol. 2011;11:91.
Adams PC. Hemochromatosis. In: Boyer TD, Manns MP, Sanyal AJ, eds. Zakim and Boyer's Hepatology: aTextbook of liver disease. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA, USA: Elsevier Saunders, 2012; p. 1127-44
Manizate F, Hiotis SP, Labow D, Roayaie S, Schwartz M. Liver functional reserve estimation: state of the artand relevance for local treatments: the Western perspective. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2010;17(4):385-8.
Morris-Stiff G, Gomez D, Prasad R. Quantitative assessment of hepatic function and its relevance to the liversurgeon. J Gastrointest Surg. 2009;13(2):374-85
Fazakas J, Mándli T, Ther G, et al. Evaluation of liver function for hepatic resection. Transplant Proc.2006;38(3):798-800.
Williams R, Aspinall R, Bellis M, et al. Addressing liver disease in the UK: a blueprint for attainingexcellence In health care and reducing premature mortality from lifestyle issues of excess consumption ofalcohol, obesity, and viral hepatitis. Lancet. 2014;384(9958):1953-97
Collaborators GmaCoD. Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortalityfor 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013.Lancet. 2015;385(9963):117-71.
Tillmann HL, McHutchison JG. Hepatitis C. In: Boyer TD, Manns MP, Sanyal AJ, eds. Zakim and Boyer'sHepatology: a Textbook of liver disease. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA, USA: Elsevier Saunders, 2012; p. -.
Manns MP, Buti M, Gane E, et al. Hepatitis C virus infection. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17006
Marchesini G, Brizi M, Bianchi G, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a feature of the metabolic syndrome.Diabetes. 2001;50(8):1844-50.
Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, Fazel Y, Henry L, Wymer M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholicfatty liver disease-Meta-Analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology.
Spinazzi A, Lorusso V, Pirovano G, KirchIn M. Safety, tolerance, biodistribution, and MR Imagingenhancement of the liver with gadobenate dimeglumine: results of clinical pharmacologic and pilot imagingstudies In nonpatient and Patient volunteers. Acad Radiol. 1999;6(5):282-91.
Gschwend S, Ebert W, Schultze- Mosgau M, Breuer J. Pharmacokinetics and imaging properties of Gd-EOB- DTPA in patients with hepatic and renal Impairment. Invest Radiol. 2011;46(9):556-66.
Leonhardt M, Keiser M, Oswald S, et al. Hepatic uptake of the magnetic resonance imaging contrast agentGd- EOB-DTPA: role of human organic anion transporters. Drug Metab Dispos. 2010;38(7):1024-8.
Pascolo L, Petrovic S, Cupelli F, et al. Abc protein transport of MRI contrast agents in canalicular rat liverplasma vesicles and yeast vacuoles. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;282(1):60-6
Ulloa JL, Stahl S, Yates J, et al. Assessment of gadoxetate DCE-MRI as a biomarker of hepatobiliarytransporter Inhibition. NMR Biomed. 2013
Fallon JK, Smith PC, Xia CQ, Kim MS. Quantification of Four Efflux Drug Transporters In Liver and KidneyAcross Species Using Targeted Quantitative Proteomics by Isotope Dilution NanoLC-MS/MS. Pharm Res.2016;33(9):2280-8
Gerdle B, Forsgren MF, Bengtsson A, et al. Decreased muscle concentrations of ATP and PCR In theQuadriceps muscle of fibromyalgia patients—a 31P-MRS study. Eur J Pain. 2013;17(8):1205-15.
Hamilton G, Middleton MS, Bydder M, et al. Effect of PRESS and STEAM sequences on magnetic resonancespectroscopic liver fat quantification. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009;30(1):145-52.
Barker PB, Bizzi A, De Stefano N, Gullapalli R, Lin DD. Clinical MR spectroscopy: Techniques andapplications. 1st ed. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 2010.
Hamilton G, Yokoo T, Bydder M, et al. In vivo characterization of the liver fat 1H MR spectrum. NMRBiomed. 2011;24(7):784-90.
Longo R, Pollesello P, Ricci C, et al. Proton MR spectroscopy In quantitative in vivo determination of fatcontent in human liver steatosis. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1995;5(3):281-5.
Reeder SB, Hu HH, Sirlin CB. Proton densIty fat-fraction: a standardized MR-based biomarker of tissue fatconcentration. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012;36(5):1011-4
Longo R, Pollesello P, Ricci C, et al. Proton MR spectroscopy in quantitative in vivo determination of fatcontent in human liver steatosis. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1995;5(3):281-5.
Reeder SB, Hu HH, Sirlin CB. Proton densIty fat-fraction: a standardized MR-based biomarker of tissue fatconcentration. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012;36(5):10 11-4
Shields GS, Coissi GS, Jimenez- Royo P, et al. Bioenergetics and intermuscular fat in chronic obstructivepulmonary disease- associated quadriceps weakness. Muscle Nerve. 2015;51(2):214-21.
Lim AK, Patel N, Hamilton G, Hajnal JV, Goldin RD, Taylor- Robinson SD. The relationship of In vivo 31PMR spectroscopy to histology in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2003;37(4):788-94.
Noren B, Lundberg P, Ressner M, Wirell S, Almer S, Smedby O. Absolute quantification of human livermetabolite concentrations by localized in vivo 31P NMR spectroscopy in diffuse liver disease. Eur Radiol.2005;15(1):148-57.
Naressi A, Couturier C, Devos JM, et al. Java-based graphical user interface for the MRUI quantitationpackage. MAGMA. 2001;12(2-3):141- 52.
Vanhamme L, A vdB, S VH. Improved method for accurate and efficient quantification of MRS data with useof prior knowledge. J Magn Reson. 1997;129(1):35-43.
Glaser KJ, Manduca A, Ehman RL. Review of MR elastography applications and recent developments. JMagn Reson Imaging. 2012;36(4):757-74.
Forsgren MF, Norén B, Kihlberg J, DahlqvIst Leinhard O, Kechagias S, Lundberg P. Comparing hepatic 2Dand 3D magnetic resonance elastography methods in a clinical setting – Initial experiences. Eur J RadiolOpen. 2015;2:66-70.
Bonate PL. Pharmacokinetic- Pharmacodynamic Modeling and Simulation. 2nd ed. New York, US: Springer,2011.
Cedersund G, Roll J. Systems biology: model based evaluation and comparison of potential explanations forgiven biological data. FEBS J. 2009;276(4):903-22
Klipp E, Liebermesiter W, Wierling C, Kowald A, Lehrach H, Herwig R. Systems biology: A textbook. 1st ed.Weinheim, Germany: WILEY- VCH Verlag Gmbh & Co., 2009Wallace K, Burt AD, Wright MC (2008)Liver fibrosis. Biochem J 411(1): 1-18.
Sporea I, Sirli R, Popescu A, Danilă M (2010) Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI)—a new modality forthe evaluation of liver fibrosis. Med Ultrason 12(1): 26-31.
European Association for Study of Liver, Asociacion Latinoamericana para el Estudio del Higadp (2015)EASL-ALEH Clinical Practice Guidelines: Non-invasive tests for evaluation of liver disease severity andprognosis. J Hepatol 63(1): 237-26
Abdollahi M, Pouri A, Ghojazadeh M, Estakhri R, Somi M (2015) Non- invasive serum fibrosis markers: Astudy In chronic hepatitis. Bioimpacts 5(1): 17-23.
Schütte K, Kipper M, Kahl S, Bornschein J, Götze T, et al. (2013) Clinical characteristics and time trends inetiology of hepatocellular cancer in Germany. Digestion 87(3): 147-159.
Bedossa P, Dargère D, Paradis V (2003) Sampling variability of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C.Hepatology 38(6): 1449-1457.
Altamirano BA, Beatriz BF, Nahum MS (2017) Management strategies for liver fibrosis. Ann Hepatol 16(1):48-56.
Cadranel JF, Rufat P, Degos F (2000) Practices of liver biopsy in France: results of a prospective nationwidesurvey. For the Group of Epidemiology of the French Association for the Study of the Liver (AFEF).Hepatology 32(3): 477-481.
Scheuer PJ, (1991) Classification of chronic viral hepatitis: a need for reassessment. J Hepatol 13(3): 372-37
Karanjia RN, Crossey MM, Cox IJ, Fye HK, Njie R, et al. (2016) Hepatic steatosis and fibrosis: Non-invasiveassessment. World J Gastroenterol 22(45): 9880-9897
Batts KP, Ludwig J (1995) Chronic hepatitis. An update on terminology and reporting. Am J Surg Pathol19(12): 1409-1417.
Seki E, Brenner DA (2015) Recent advancement of molecular mechanisms of liver fibrosis. J HepatobiliaryPancreat Sci 22(7): 512-528.
Wai CT, Greenson JK, Fontana RJ, Kalbfleisch JD, Marrero JA, et al. (2003) A simple noninvasive Index canpredict both significant fibrosis and cirrhosis In patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 38(2): 518-
Tacke F, Weiskirchen R (2010) Liver fibrosis – pathogenesis and novel therapeutic approaches. Internist(Berl) 51(1): 21-29. 526.
Balogh J, Victor D, Asham EH, Burroughs SG, Boktour M, et al. (2016) 29. Bedossa P, Poynard T (1996) Analgorithm for the grading of activity Hepatocellular carcinoma: a review. J Hepatocell Carcinoma 3: 41-53
Aghemo A, Colombo M (2013) Hepatocellular carcinoma In chronic hepatitis C: from bench to bedside.Semin Immunopathol 35(1): 111-120
Ishak K, Baptista A, Bianchi L, Callea F, De Groote J, et al. (1995) Histological grading and staging ofchronic hepatitis. J Hepatol 22(6).
Paradis V (2013) Histopathology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Recent Results Cancer Res 190: 21-32.
Angulo P, Hui JM, Marchesini G, BugIanesI E, George J, et al. (2007) The NAFLD fibrosis score: anoninvasive system that Identifies liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD. Hepatology 45(4): 846-854.
Lencioni R, Kudo M, Ye SL, Bronowicki JP, Chen XP, et al. (2012) First interim analysis of the GIDEON(Global Investigation of therapeutic decisions in hepatocellular carcinoma and of Its treatment with sorafeNib) non-interventional study. Int J Clin Pract 66(7): 675-683.
WanlessIR, Sweeney G, Dhillon AP, Guido M, Piga A, et al. (2002) Lack of progressive hepatic fibrosisduring long-term therapy with deferiprone in subjects with transfusion-dependent beta-thalassemia. Blood100(5): 1566-1569.
Xu J, Murphy SL, Kochanek KD, Bastian BA (2016) Deaths: Final Data for 2013. Natl Vital Stat Rep 64(2):1-119
Brunt EM, Janney CG, Di Bisceglie AM, Neuschwander-TBA, Bacon BR (1999) Nonalcoholicsteatohepatitis: a proposal for grading and staging the histological lesions. Am J Gastroenterol 94(9): 2467-2474.
O'Regan DP, Callaghan MF, Wylezinska-Arridge M, et al. Liver fat content and T2*: simultaneous measurement by using breath-hold multiecho MR imaging at 3.0 T—feasibility. Radiology. 2008;247(2):550-7.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Current Clinical and Medical Education