Isolation and Identification of Bacterial Burn Wound Infection and Their Antimicrobial Resistance
Keywords:
Burn Wound, Infection, Bacteria, Antimicrobial ResistanceAbstract
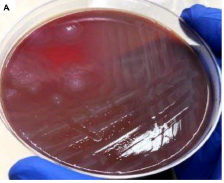
Burns constitute a major role in mortality and morbidity in the whole world, whether accidental, suicidal or homicidal. Burn injuries are among the most devastating of all injuries and a major global public health crisis Burns are the fourth most common type of trauma worldwide, following traffic accidents, falls, and inter personal violence. Bacterial infections are serious problem among burns patients and P.aeruginosa has emerged as the commonest organism causing infection and is resistant to most of the antibiotics.
Downloads
References
Othman, N. (2010). Epidemiology of burn injuries in Sulaymaniyah province of Iraq (Doctoral dissertation, University of Nottingham)pp.56.
Santos, J. V., Oliveira, A., Costa-Pereira, A., Amarante, J., & Freitas, A. (2016). Burden of burns in Portugal, 2000-2013: a clinical and economic analysis of 26,447 hospitalisations. Burns, 42(4), 891-900.
Mayhall, C. G. (2012). Hospital epidemiology and infection control. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins..
Chen, Y. Y., Wu, P. F., Chen, C. S., Chen, I. H., Huang, W. T., & Wang, F. D. (2020). Trends in microbial profile of burn patients following an event of dust explosion at a tertiary medical center. BMC infectious diseases, 20(1), 1-11.
Siegel JD, Rhinehart E, Jackson M, Chiarello L,. (0226). Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory C. Management of multidrug-resistant organisms in health care settings.. Am J Infect Control. 2007;35:S165-93.
Weber, J., McManus, A., & Nursing Committee of the International Society for Burn Injuries. (2004). Infection control in burn patients. Burns, 30(8), A16-A24.
Ronat, J. B., Kakol, J., Khoury, M. N., Berthelot, M., Yun, O., Brown, V., & Murphy, R. A. (2014). Highly drug-resistant pathogens implicated in burn-associated bacteremia in an Iraqi burn care unit. PloS one, 9(8), e101017.
Devrim, İ., Kara, A., Düzgöl, M., Karkıner, A., Bayram, N., Temir, G., & Hoşgör, M. (2017). Burn-associated bloodstream infections in pediatric burn patients: time distribution of etiologic agents. Burns, 43(1), 144-148.
Ramirez-Blanco, C. E., Ramirez-Rivero, C. E., Diaz-Martinez, L. A., & Sosa-Avila, L. M. (2017). Infection in burn patients in a referral center in Colombia. Burns, 43(3), 642-653.
Merchant, N., Smith, K., & Jeschke, M. G. (2015). An ounce of prevention saves tons of lives: infection in burns. Surgical Infections, 16(4), 380-387.
Siegel, J. D., Rhinehart, E., Jackson, M., & Chiarello, L. (2007). 2007 guideline for isolation precautions: preventing transmission of infectious agents in health care settings. American journal of infection control, 35(10), S65-S164.
Lachiewicz, A. M., van Duin, D., DiBiase, L. M., Jones, S. W., Carson, S., Rutala, W. A., & Weber, D. J. (2015). Rates of hospital- associated respiratory infections and associated pathogens in a regional burn center, 2008-2012. infection control & hospital epidemiology, 36(5), 601- 603..
Chen, Y. Y., Chou, Y. C., & Chou, P. (2005). Impact of nosocomial infection on cost of illness and length of stay in intensive care units. Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology, 26(3), 281-287.. –
Chen, Y. Y., Wang, F. D., Liu, C. Y., & Chou, P. (2009). Incidence rate and variable cost of nosocomial infections in different types of intensive care units. Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology, 30(1), 39-46..
Hop, M. J., Polinder, S., van der Vlies, C. H., Middelkoop, E., & van Baar, M. E. (2014). Costs of burn care: a systematic review. Wound repair and regeneration, 22(4), 436-450.
Manson, W. L., Pernot, P. C. J., Fidler, V., Sauer, E. W., & Klasen, H. J. (1992). Colonization of burns and the duration of hospital stay of severely burned patients. Journal of hospital Infection, 22(1), 55-63.
Lari, A. R., & Alaghehbandan, R. (2000). Nosocomial infections in an Iranian burn care center. Burns, 26(8), 737-740.
Boyer, F., Couturier, É., Pouliquen, O., & Guazzelli, É. (2015). Suspensions in a tilted trough: second normal stress difference. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 686, 26-39.
Okon E., Uboh, F. I. E., & Ekong, M. B. (2014). Effect of aqueous extract of Psidium guajava leaves on liver enzymes, histological integrity and hematological indices in rats. Gastroenterology Research, 3(1), 32.
Kandati, S., Flack, K. L., Agarwal, P., & Selfe, T. K. (2015). The association of restless legs syndrome to history of gestational diabetes in an Appalachian primary care population. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, 11(10), 1121-1130.
Adugna, A., Kibret, M., Abera, B., Nibret, E., & Adal, M. (2015). Antibiogram of E. coli serotypes isolated from children aged under five with acute diarrhea in Bahir Dar town. African health sciences, 15(2), 656-664.
Bowler, P. G., & Davies, B. J. (1999). The microbiology of infected and noninfected leg ulcers.
Hakim, E. H., Achmad, S. A., Juliawaty, L. D., Makmur, L., Syah, Y. M., Aimi, N., & Ghisalberti, E. L. (2016). Prenylated flavonoids and ... related compounds of the Indonesian Artocarpus (Moraceae). Journal of Natural Medicines, 60(3), 161-184.
Panjeshahin, M. R., Lari, A. R., Talei, A. R., Shamsnia, J., & Alaghehbandan, R. (2011). Epidemiology and mortality of burns in the South West of Iran. Burns, 27(3), 219-226.
Bujok, G. (2010). Haemodynamic Disorders in the Course of Electrical Burns. A Preliminary Report. Annals of Burns and Fire Disasters, 19(1), 36.
Prestinaci, F., Pezzotti, P., and Pantosti, A. (2015). Antimicrobial resistance: a global multifaceted phenomenon. Pathogens and global health, 109(7), 309.
Talaiekhozani, A., Alaee, S., and Ponraj, M. (2015). Guidelines for quick application of biochemical tests to identify unknown bacteria. AOBR, 2(2), 65-82.
Lob, S. H., Nicolle, L. E., Hoban, D. J., Kazmierczak, K. M., Badal, R. E., and Sahm, D. F. (2016). Susceptibility patterns and ESBL rates of Escherichia coli from urinary tract infections in Canada and the United States, SMART 2010-2014. Diagnostic microbiology and infectious disease, 85(4), 459-465.
Hrbacek, J., Cermak, P., and Zachoval, R. (2020). Current antibiotic resistance trends of uropathogens in Central Europe: Survey from a Tertiary hospital urology department 2011-2019. Antibiotics, 9(9), 630.#
Varela, M. F., Stephen, J., Lekshmi, M., Ojha, M., Wenzel, N., Sanford, L. M., and Kumar, S. H. (2021). Bacterial Resistance to Antimicrobial Agents. Antibiotics, 10(5), 593.#
Iacchini, S., Korbekandi, H., Mirmohammadi, S. V., and Zolfaghari, B. (2019). Synthesis of silver nanoparticles: chemical, physical and biological methods. Research in pharmaceutical sciences, 9(6), 385.
Francois, M., Hanslik, T., Dervaux, B., Le Strat, Y., Souty, C., Vaux, S., and Rossignol, L. (2016). The economic burden of urinary tract infections in women visiting general practices in France: a cross-sectional survey. BMC health services research, 16(1), 1-
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Current Clinical and Medical Education