Characteristics, Risk Factors, and Associated Complications of Diabetic Patients Attending Al-Wafaa Diabetes Center, Mosul: An Analytical Cross-Sectional Study
Keywords:
Diabetes, Risk factors, studyAbstract
- Background: Diabetes mellitus represents a significant health challenge in post-conflict regions like Mosul, Iraq, where population-specific data remains limited.
Objective: To examine demographic characteristics, risk factors, complications, and analyze associations between modifiable risks and complication onset among diabetic patients.
Methods: An analytical cross-sectional study was conducted at Al-Wafaa Diabetes Center from October 2023 to March 2024. A simple random sample of 140 diabetic patients was recruited. Data were collected via structured questionnaires and medical records. Descriptive statistics and logistic regression analyses were performed using SPSS v24.
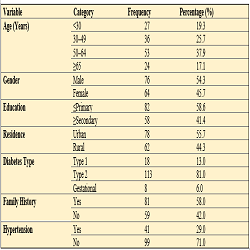
Results: The mean age was 48.96 ± 14.42 years, with 54.3% males. Type 2 diabetes predominated (81%). Key findings included: 76% of participants reported no physical activity; 57.1% were overweight/obese. Prevalent complications were retinopathy (27.1%), cardiovascular disease (25.7%), and neuropathy (25.0%). Neuropathy developed earliest (7.9 ± 3.5 years; p=0.023). Physical inactivity significantly increased neuropathy risk (aOR=2.5; 95% CI: 1.2–5.3), and obesity independently predicted cardiovascular disease (aOR=2.8; 95% CI: 1.3–6.2).
Conclusion: Sedentary lifestyle and obesity are strongly linked to complications, with neuropathy manifesting earliest. Early screening and targeted lifestyle interventions are urgently needed.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Lubnah Shaker Mahmood, Mohammad Salih Alkaisy, Salim Shihab Almetewty

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Current Clinical and Medical Education