Establishing a Standardized Professional Endurance Assessment Framework for U19 Male Basketball Athletes in Da Nang, Vietnam
Keywords:
Professional endurance, U19 basketball, VO2 max, Beep Test, Cosmed K4b2, assessment scale, sports trainingAbstract
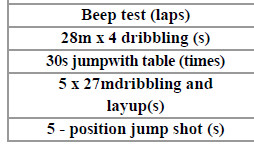
This study aimed to design and rigorously assess the effectiveness of an eight-week periodized professional endurance (PE) training intervention for U19 male basketball athletes in Da Nang, Vietnam. Grounded in Bompa’s periodization theory and informed by expert consensus (>80%), the program incorporated thirty basketball-specific endurance exercises executed over two distinct phases: anatomical adaptation (weeks 1–4) and maximal endurance development (weeks 5–8). Twenty athletes (mean age 17.9 ± 0.5 years) underwent pre- and post-intervention assessments encompassing five field-based PE tests and dual-mode VO₂max measurements (Beep Test and Cosmed K4b2). Post-intervention, significant enhancements were observed across all PE metrics, with performance increases ranging from 8.2% to 17.0% (p < 0.001) and VO₂max improvements of 7.7% (47.9 → 51.6 ml·kg⁻¹·min⁻¹) and 8.5% (48.2 → 52.3 ml·kg⁻¹·min⁻¹) via Beep Test and Cosmed K4b2, respectively. The proportion of athletes achieving 'Excellent' endurance levels rose from 10% to 30–60%. These findings substantiate the program’s capacity to elevate aerobic capacity and sport-specific endurance, offering a scientifically grounded framework for optimizing youth basketball training.
Downloads
References
Amasuomo, A. C., & Okoro, J. O. (2019). Effects of high-intensity interval training on aerobic capacity of basketball players. International Journal of Physical Education, Sports and Health, 6(3), 45-50.
Åstrand, P. O., & Rodahl, K. (2003). Textbook of work physiology: Physiological bases of exercise (4th ed.). Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics.
Ben Abdelkrim, N., El Fazaa, S., & El Ati, J. (2007). Time-motion analysis and physiological data of elite under-19 basketball players during competition. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 41(2), 69-75. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsm.2006.032318
Bo chinh tri. (2007). Nghi quyet so 08-NQ/TW ve tang cuong su lanh dao cua Dangtao buoc phat trien manh me ve the duc, the thao den nam 2020. Ha Noi, Viet Nam.
Brooks, G. A., Fahey, T. D., & Baldwin, K. M. (2005). Exercise physiology: Human bioenergetics and its applications (4th ed.). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
Castagna, C., Manzi, V., D’Ottavio, S., Annino, G., Padua, E., & Bishop, D. (2010). Relation between maximal aerobic power and the ability to repeat sprints in young basketball players. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 24(4), 1035-1040. https://doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181cc236f
Costill, D. L., & Wilmore, J. H. (2015). Physiology of sport and exercise (6th ed.). Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics.
Drinkwater, E. J., Pyne, D. B., & McKenna, M. J. (2008). Design and interpretation of anthropometric and fitness testing of basketball players. Sports Medicine, 38(4), 351-363. https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-200838040-00005
Fox, J. L., Stanton, R., & Scanlan, A. T. (2018). A comparison of training and physical performance variables between small-sided games and regular basketball training. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 32(8), 2239-2246. https://doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0000000000002608
Hawley, J. A. (2000). Training for endurance. Oxford, UK: Blackwell Science.
Hoffman, J. R. (2006). Norms for fitness, performance, and health. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics.
Laursen, P. B., & Jenkins, D. G. (2002). The scientific basis for high-intensity interval training: Optimising training programmes and maximising performance in highly trained endurance athletes. Sports Medicine, 32(1), 53-73. https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-200232010-00003
Léger, L. A., Mercier, D., Gadoury, C., & Lambert, J. (1988). The multistage 20 metre shuttle run test for aerobic fitness. Journal of Sports Sciences, 6(2), 93-101. https://doi.org/10.1080/02640418808729800
McInnes, S. E., Carlson, J. S., Jones, C. J., & McKenna, M. J. (1995). The physiological load imposed on basketball players during competition. Journal of Sports Sciences, 13(5), 387-397. https://doi.org/10.1080/02640419508732254
Nguyen Van Hung. (2018). Nghien cuu suc ben chuyen mon cua van dong vien bong ro U18 Viet Nam. Tap chi khoa hoc the thao Viet Nam, 45(2), 12-18.
Ross, R., Blair, S. N., Arena, R., Church, T. S., Després, J. P., Franklin, B. A., Haskell, W. L., Kaminsky, L. A., Levine, B. D., Lavie, C. J., Myers, J., Niebauer, J., Sallis, R., Sawada, S. S., Sui, X., & Wisløff, U. (2016). Importance of assessing cardiorespiratory fitness in clinical practice: A case for fitness as a clinical vital sign: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation, 134(24), e653-e699. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000461
Scanlan, A. T., Dascombe, B. J., Reaburn, P., & Dalbo, V. J. (2014). The physiological and activity demands experienced by Australian female basketball players during competition. Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport, 17(3), 341-347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsams.2013.05.008
Singh, R., & Boyle, R. (2020). Aerobic endurance (VO2 max) in elite Indian basketball players: A cross-sectional study. International Journal of Creative Research Thoughts, 8(12), 2345-2352. Retrieved from https://www.ijcrt.org/papers/IJCRT2012245.pdf
Stojanović, E., Stojiljković, N., Scanlan, A. T., Dalbo, V. J., Berkelmans, D. M., & Milanović, Z. (2018). The activity demands and physiological responses encountered during basketball match-play: A systematic review. Sports Medicine, 48(1), 111-135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-017-0798-8
The Movement System. (2022, August 6). What is a good VO2 max? The Movement System. Retrieved from https://www.themovementsystem.com/blog/what-is-a-good-vo2-max
Tran Quoc Cuong. (2020). Danh gia the luc van dong vien bóng ro nam Dai hoc TDTT TP.HCM. Tap chi the thao, 52(1), 25-31.
Ziv, G., & Lidor, R. (2009). Physical attributes, physiological characteristics, on-court performances and nutritional strategies of female and male basketball players. Sports Medicine, 39(7), 547-568. https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-200939070-00003
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Current Clinical and Medical Education