Ulcerative Colitis: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Overall Management of Adult Patients
Keywords:
Ulcerative Colitis, Diagnosis, Treatment, PatientsAbstract
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is an inflammatory chronic disease primarily affecting the
colonic mucosa; the extent and severity of colon involvement are variable. In its most limited
form it may be restricted to the distal rectum, while in its most extended form the entire
colon is involved. UC belongs to the inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), which is a general
term for a group of chronic inflammatory disorders of unknown etiology involving the
gastrointestinal tract. UC is usually associated with recurrent attacks with complete
remission of symptoms in the interim. In Western Europe and in the USA, UC has an
incidence of approximately 6 to 8 cases per 100.000 populations and an estimated prevalence
of approximately 70 to 150 per 100.000 populations. The leading initial symptom of UC is
diarrhea with blood and mucus, sometimes with pain. Fever and weight loss are less
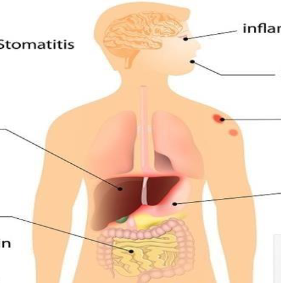
frequent. Extra intestinal symptoms can be an initial manifestation or can occur later in the
course of the disease. Eighty percent of the patients have only proctitis or proctosigmoiditis,
and only 20% have extensive colitis. However, in about 50% of patients with initial
proctosigmoiditis, proximal extension occurs later, and in some patients the opposite takes
place. Depending of the stage of the disease, endoscopy reveals reddening of the mucosa,
increased vulnerability, mucosal bleeding, irregular ulcers, pseudo polyps, granularity, and
loss of vascular architecture. Several drugs interacting with various points along the immune
and inflammatory cascades are currently available for the treatment of UC. Corticosteroids,
amino salicylates, immunomodulators are the mainstay of medical treatment otherwise
surgery recommended which may be radical.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Current Clinical and Medical Education