Characterization of Bioactive Metabolites Released from Proteus mirabilis isolated from UTI patients and Evaluation of Antibacterial activity Using Trigonella foenum-graecum, Petroselinum crispum, and Hordeum vulgare Medicinal Plants
Keywords:
Proteus mirabilis, Bioactive metabolites, AntibacterialAbstract
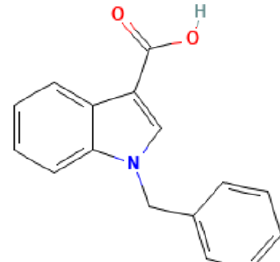
Proteus mirabilis is a Gram-negative bacterium which is well-known for its ability to robustly swarm across surfaces in a striking bulls’-eye pattern. Clinically, this organism is most frequently a pathogen of the urinary tract, particularly in patients undergoing long-term catheterization. P. mirabilis with a focus on urinary tract infections (UTI), including disease models, vaccine development efforts, and clinical perspectives. The purpose of this study was to : Investigate the antibacterial effects of the medicinal herbs Trigonella foenum-graecum, Petroselinum crispum, and Hordeum vulgare by analyzing the bioactive volatile compounds generated by Proteus mirabilis. Materials and Methods: The isolates were diagnosed as Proteus mirabilis species based on the findings of non-lactose fermenting colonies on MacConkey agar with swarming on blood agar plate, characteristic fishy smell, microscopic examination show gram negative pleomorphic bacilli with active motility and the results of biochemical tests were negative for Gram stain, Oxidase and Indol. While, were positive for Catalase, Methyl red, Voscproscouer, Citrate and Urease. An Agilent 789 A instrument was used to perform the examination, which was performed using a GC–MS approach. Results: GC-MS analysis of Proteus mirabilis found: Ethylsulfonylpropanone, Pyrazolo[1.5-a]pyridine , 3-methyl-2-phenyl, 3-Methyl-2-phenylbutanal, 1- Benzylindole-3-carboxylic acid, L-proline, 1-cyclohexanecarbonylpiperidin-4-amine, 2,4-dimethyl-4-phenyloxolane, mono-Methyl isophthalate, 3-(benzyloxymethyl)cyclobutanone, 1-(4-methoxyphenoxy)propan-2-amine, and 2-cyclopropylpropan-2-amine. In vitro antimicrobial activity of three plant extracts on Proteus mirabilis: The inhibition zone (mm) of bioactive components of Trigonella foenum-graecum, Petroselinum crispum, and Hordeum vulgare medicinal plants ethanolic, and ethyl acetate, extract comparison with Vancomycin (standard antibiotics) against Proteus mirabilis was recorded as follows: 19.71±0.25, 15.00±0.21 and 23.09±0.16 mm respectively for Trigonella foenum-graecum. While recorded 16.00±0.23, 10.81±0.11 and 23.09±0.16 mm respectively for Petroselinum crispum. In vitro antimicrobial activity of plant extracts on Proteus mirabilis recorded 15.04±0.21, 09.00±0.01 and 23.09±0.16 mm respectively for Hordeum vulgare. Trigonella foenum-graecum 19.71±0.25 mm was very highly active against Proteus mirabilis.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Current Clinical and Medical Education